|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .github | ||
| diagrams | ||
| dist | ||
| test | ||
| typings/merkletreejs | ||
| .editorconfig | ||
| .gitattributes | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .npmignore | ||
| .travis.yml | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
| index.ts | ||
| jsdoc.js | ||
| package-lock.json | ||
| package.json | ||
| tsconfig.json | ||
README.md
MerkleTree.js
Construct Merkle Trees and verify proofs in JavaScript.
Contents
Diagrams
Diagram of Merkle Tree

Diagram of Merkle Tree Proof

Diagram of Invalid Merkle Tree Proofs
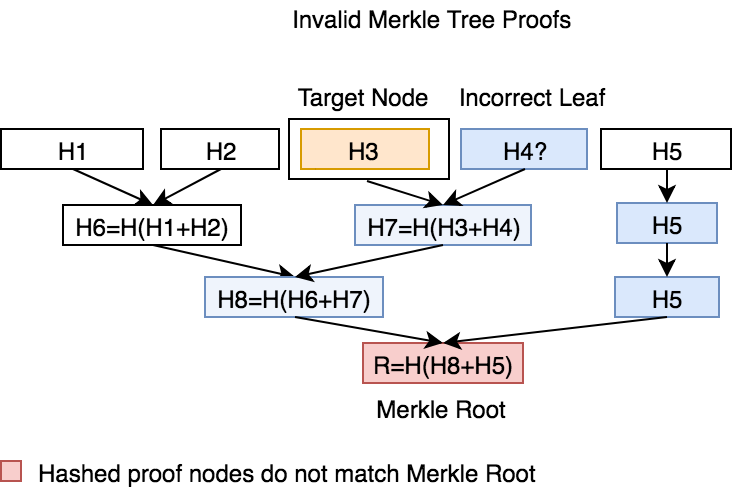
Diagram of Bitcoin Merkle Tree

Install
npm install merkletreejs
Getting started
Construct tree, generate proof, and verify proof:
const { MerkleTree } = require('merkletreejs')
const SHA256 = require('crypto-js/sha256')
const leaves = ['a', 'b', 'c'].map(x => SHA256(x))
const tree = new MerkleTree(leaves, SHA256)
const root = tree.getRoot().toString('hex')
const leaf = SHA256('a')
const proof = tree.getProof(leaf)
console.log(tree.verify(proof, leaf, root)) // true
const badLeaves = ['a', 'x', 'c'].map(x => SHA256(x))
const badTree = new MerkleTree(badLeaves, SHA256)
const badLeaf = SHA256('x')
const badProof = tree.getProof(badLeaf)
console.log(tree.verify(badProof, leaf, root)) // false
Print tree to console:
MerkleTree.print(tree)
Output
└─ 311d2e46f49b15fff8b746b74ad57f2cc9e0d9939fda94387141a2d3fdf187ae
├─ 176f0f307632fdd5831875eb709e2f68d770b102262998b214ddeb3f04164ae1
│ ├─ 3ac225168df54212a25c1c01fd35bebfea408fdac2e31ddd6f80a4bbf9a5f1cb
│ └─ b5553de315e0edf504d9150af82dafa5c4667fa618ed0a6f19c69b41166c5510
└─ 0b42b6393c1f53060fe3ddbfcd7aadcca894465a5a438f69c87d790b2299b9b2
└─ 0b42b6393c1f53060fe3ddbfcd7aadcca894465a5a438f69c87d790b2299b9b2
Documentation
Classes
Objects
- MerkleTree :
object Class reprensenting a Merkle Tree
MerkleTree
Kind: global class
- MerkleTree
- new MerkleTree(leaves, hashAlgorithm, options)
- .getLeaves() ⇒
Array.<Buffer> - .getLayers() ⇒
Array.<Buffer> - .getRoot() ⇒
Buffer - .getProof(leaf, [index]) ⇒
Array.<Object> - .verify(proof, targetNode, root) ⇒
Boolean
new MerkleTree(leaves, hashAlgorithm, options)
Constructs a Merkle Tree. All nodes and leaves are stored as Buffers. Lonely leaf nodes are promoted to the next level up without being hashed again.
| Param | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| leaves | Array.<Buffer> |
Array of hashed leaves. Each leaf must be a Buffer. |
| hashAlgorithm | function |
Algorithm used for hashing leaves and nodes |
| options | Object |
Additional options |
| options.isBitcoinTree | Boolean |
If set to true, constructs the Merkle Tree using the Bitcoin Merkle Tree implementation. Enable it when you need to replicate Bitcoin constructed Merkle Trees. In Bitcoin Merkle Trees, single nodes are combined with themselves, and each output hash is hashed again. |
Example
const { MerkleTree } = require('merkletreejs')
const crypto = require('crypto')
function sha256(data) {
// returns Buffer
return crypto.createHash('sha256').update(data).digest()
}
const leaves = ['a', 'b', 'c'].map(x => sha256(x))
const tree = new MerkleTree(leaves, sha256)
merkleTree.getLeaves() ⇒ Array.<Buffer>
Returns array of leaves of Merkle Tree.
Kind: instance method of MerkleTree
Example
const leaves = tree.getLeaves()
merkleTree.getLayers() ⇒ Array.<Buffer>
Returns array of all layers of Merkle Tree, including leaves and root.
Kind: instance method of MerkleTree
Example
const layers = tree.getLayers()
merkleTree.getRoot() ⇒ Buffer
Returns the Merkle root hash as a Buffer.
Kind: instance method of MerkleTree
Example
const root = tree.getRoot()
merkleTree.getProof(leaf, [index]) ⇒ Array.<Object>
Returns the proof for a target leaf.
Kind: instance method of MerkleTree
Returns: Array.<Object> - - Array of objects containing a position property of type string with values of 'left' or 'right' and a data property of type Buffer.
| Param | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| leaf | Buffer |
Target leaf |
| [index] | Number |
Target leaf index in leaves array. Use if there are leaves containing duplicate data in order to distinguish it. |
Example
const proof = tree.getProof(leaves[2])
Example
const leaves = ['a', 'b', 'a'].map(x => sha256(x))
const tree = new MerkleTree(leaves, sha256)
const proof = tree.getProof(leaves[2], 2)
merkleTree.verify(proof, targetNode, root) ⇒ Boolean
Returns true if the proof path (array of hashes) can connect the target node to the Merkle root.
Kind: instance method of MerkleTree
| Param | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| proof | Array.<Object> |
Array of proof objects that should connect target node to Merkle root. |
| targetNode | Buffer |
Target node Buffer |
| root | Buffer |
Merkle root Buffer |
Example
const root = tree.getRoot()
const proof = tree.getProof(leaves[2])
const verified = tree.verify(proof, leaves[2], root)
MerkleTree : object
Class reprensenting a Merkle Tree
Kind: global namespace
- MerkleTree :
object- new MerkleTree(leaves, hashAlgorithm, options)
- .getLeaves() ⇒
Array.<Buffer> - .getLayers() ⇒
Array.<Buffer> - .getRoot() ⇒
Buffer - .getProof(leaf, [index]) ⇒
Array.<Object> - .verify(proof, targetNode, root) ⇒
Boolean
new MerkleTree(leaves, hashAlgorithm, options)
Constructs a Merkle Tree. All nodes and leaves are stored as Buffers. Lonely leaf nodes are promoted to the next level up without being hashed again.
| Param | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| leaves | Array.<Buffer> |
Array of hashed leaves. Each leaf must be a Buffer. |
| hashAlgorithm | function |
Algorithm used for hashing leaves and nodes |
| options | Object |
Additional options |
| options.isBitcoinTree | Boolean |
If set to true, constructs the Merkle Tree using the Bitcoin Merkle Tree implementation. Enable it when you need to replicate Bitcoin constructed Merkle Trees. In Bitcoin Merkle Trees, single nodes are combined with themselves, and each output hash is hashed again. |
Example
const { MerkleTree } = require('merkletreejs')
const crypto = require('crypto')
function sha256(data) {
// returns Buffer
return crypto.createHash('sha256').update(data).digest()
}
const leaves = ['a', 'b', 'c'].map(x => sha256(x))
const tree = new MerkleTree(leaves, sha256)
merkleTree.getLeaves() ⇒ Array.<Buffer>
Returns array of leaves of Merkle Tree.
Kind: instance method of MerkleTree
Example
const leaves = tree.getLeaves()
merkleTree.getLayers() ⇒ Array.<Buffer>
Returns array of all layers of Merkle Tree, including leaves and root.
Kind: instance method of MerkleTree
Example
const layers = tree.getLayers()
merkleTree.getRoot() ⇒ Buffer
Returns the Merkle root hash as a Buffer.
Kind: instance method of MerkleTree
Example
const root = tree.getRoot()
merkleTree.getProof(leaf, [index]) ⇒ Array.<Object>
Returns the proof for a target leaf.
Kind: instance method of MerkleTree
Returns: Array.<Buffer> - - Array of objects containing a position property of type string with values of 'left' or 'right' and a data property of type Buffer.
| Param | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| leaf | Buffer |
Target leaf |
| [index] | Number |
Target leaf index in leaves array. Use if there are leaves containing duplicate data in order to distinguish it. |
Example
const proof = tree.getProof(leaves[2])
Example
const leaves = ['a', 'b', 'a'].map(x => sha256(x))
const tree = new MerkleTree(leaves, sha256)
const proof = tree.getProof(leaves[2], 2)
merkleTree.verify(proof, targetNode, root) ⇒ Boolean
Returns true if the proof path (array of hashes) can connect the target node to the Merkle root.
Kind: instance method of MerkleTree
| Param | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| proof | Array.<Buffer> |
Array of proof Buffer hashes that should connect target node to Merkle root. |
| targetNode | Buffer |
Target node Buffer |
| root | Buffer |
Merkle root Buffer |
Example
const root = tree.getRoot()
const proof = tree.getProof(leaves[2])
const verified = tree.verify(proof, leaves[2], root)
Test
npm test
FAQ
- Q: How do you verify merkle proofs in Solidity?
- A: Check out the example repo merkletreejs-solidity on how to generate merkle proofs with this library and verify them in Solidity.
Notes
As is, this implemenation is vulnerable to a second pre-image attack. Use a difference hashing algorithm function for leaves and nodes, so that H(x) != H'(x).
Also, as is, this implementation is vulnerable to a forgery attack for an unbalanced tree, where the last leaf node can be duplicated to create an artificial balanced tree, resulting in the same Merkle root hash. Do not accept unbalanced tree to prevent this.
More info here.
Resources
-
Bitcoin mining the hard way: the algorithms, protocols, and bytes
-
Why aren't Solidity sha3 hashes not matching what other sha3 libraries produce?
-
What is the purpose of using different hash functions for the leaves and internals of a hash tree?

