|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| bind | ||
| client | ||
| cmd | ||
| codebase | ||
| config | ||
| git | ||
| images | ||
| mount | ||
| scripts | ||
| workspace | ||
| README.md | ||
| go.mod | ||
README.md
hacksaw
HACK in a Speedy Access Workspace
What is Hacksaw?
If you have a large multi-gigabyte codebase spread out through multiple git projects it can take a long time branch off a clean workspace. Hacksaw is a tool that lets you split off a clean workspace in seconds. It does so by only copying git projects that you explicitly select to be edited. All other projects are read-only bind mounts. This lets you build without cloning the full codebase to a new location!
How much faster is it, really?
Lets look at some performance numbers for creating a hacksaw workspace using as a codebase the AOSP master branch as of 2020-8-4. The machine used was a c2-standard-60 Google Cloud Platform VM with 60 vCPUs and 240 GiB of RAM. Each action was performed at least 10 times then averaged out.
-
Create a new Hacksaw workspace
- Time: 0.4 sec
- Disk usage: 7.9 MiB
-
Remove a Hacksaw workspace with no edits or build artifacts.
- Time: 0.6 sec
-
Create a new Hacksaw workspace and edit build/make project.
- Time: 0.6 sec
- Disk usage: 18 MiB
-
Create a new Hacksaw workspace and edit frameworks/base project.
- Time: 7.5 sec
- Disk usage: 1.3 GiB
As you can see, the time it takes to set up a new hacksaw workspace is proportional to the git projects checked out for editing. Contrast that with how long it takes to create a workspace using a full repo sync with a local mirror.
-
Create a new full repo workspace using a fresh local mirror
- Time: 12 min 32 sec
- Disk usage: 88 GiB
-
Remove a full repo workspace with no build artifacts
- Time: 28 seconds
Can you give me an example?
$ mkdir ~/aosp
$ cd ~/aosp
$ repo init -u https://android.googlesource.com/platform/manifest
...
$ repo sync --quiet --current-branch --no-tags --no-clone-bundle --jobs=$(nproc)
...
$ hacksaw codebase add aosp ~/aosp
Added codebase aosp
$ hacksaw codebase default aosp
Default codebase set to aosp
$ hacksaw workspace new big-feature
Composing.................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
...........................................
Workspace composed
Created big-feature at ~/hacksaw/big-feature
$ hacksaw edit ~/hacksaw/big-feature/tools/treble
Created branch big-feature on project ~/hacksaw/big-feature/tools/treble
$ hacksaw workspace new quick-fix
Composing.................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
...........................................
Workspace composed
Created big-feature at ~/hacksaw/quick-fix
$ hacksaw edit ~/hacksaw/quick-fix/tools/treble
Created branch quick-fix on project ~/hacksaw/quick-fix/tools/treble
How do I install it?
Building hacksaw requires golang to be installed. To install the hacksaw client run the following:
go get android.googlesource.com/platform/tools/treble.git/hacksaw/cmd/hacksaw
This will install hacksaw to ~/go/bin/hacksaw. You may choose to copy that to a location in your path. For example:
sudo cp ~/go/bin/hacksaw /usr/local/bin
sudo chmod 755 /usr/local/bin/hacksaw
How do I make sure that creating a hacksaw workspace is fast?
Hacksaw creates bind mounts for all git projects in a codebase. It then copies everything else. Make sure you remove all build artifacts from a codebase before create a workspace, otherwise it may spend a long time copying them.
How do I run it with sudo?
Commands that mount and unmount will require sudo. That includes commands like
hacksaw workspace newhacksaw edithacksaw workspace remove
Other commmands like hacksaw workspace list or hacksaw add codebase do not
mount or unmount so do not require sudo.
If you would like to avoid using sudo you may install hacksawd as explained below.
How do I run it without sudo?
Hacksawd is a privileged system daemon whose only job is to manage bind mounts. The provided install script will install to your system
go get android.googlesource.com/platform/tools/treble.git/hacksaw/cmd/hacksawd
sudo cp ~/go/bin/hacksawd /usr/local/bin
sudo chmod 755 /usr/local/bin/hacksawd
sudo ~/go/src/android.googlesource.com/platform/tools/treble.git/hacksaw/scripts/install-service.sh
The installation scripts creates a new "hacksaw" group and adds you to it. You will need to log out and log back in for the group changes to take effect. After that you should be able to run any hacksaw command without sudo.
If you wish to uninstall the service then run:
sudo ~/go/src/android.googlesource.com/platform/tools/treble.git/hacksaw/scripts/uninstall-service.sh
sudo rm /usr/local/bin/hacksawd
How do I sync?
You sync your codebases using repo sync. All updates will be propagated to workspaces.
Except for projects that you are currently editing. Those will require you to git pull
manually in the workspace project.
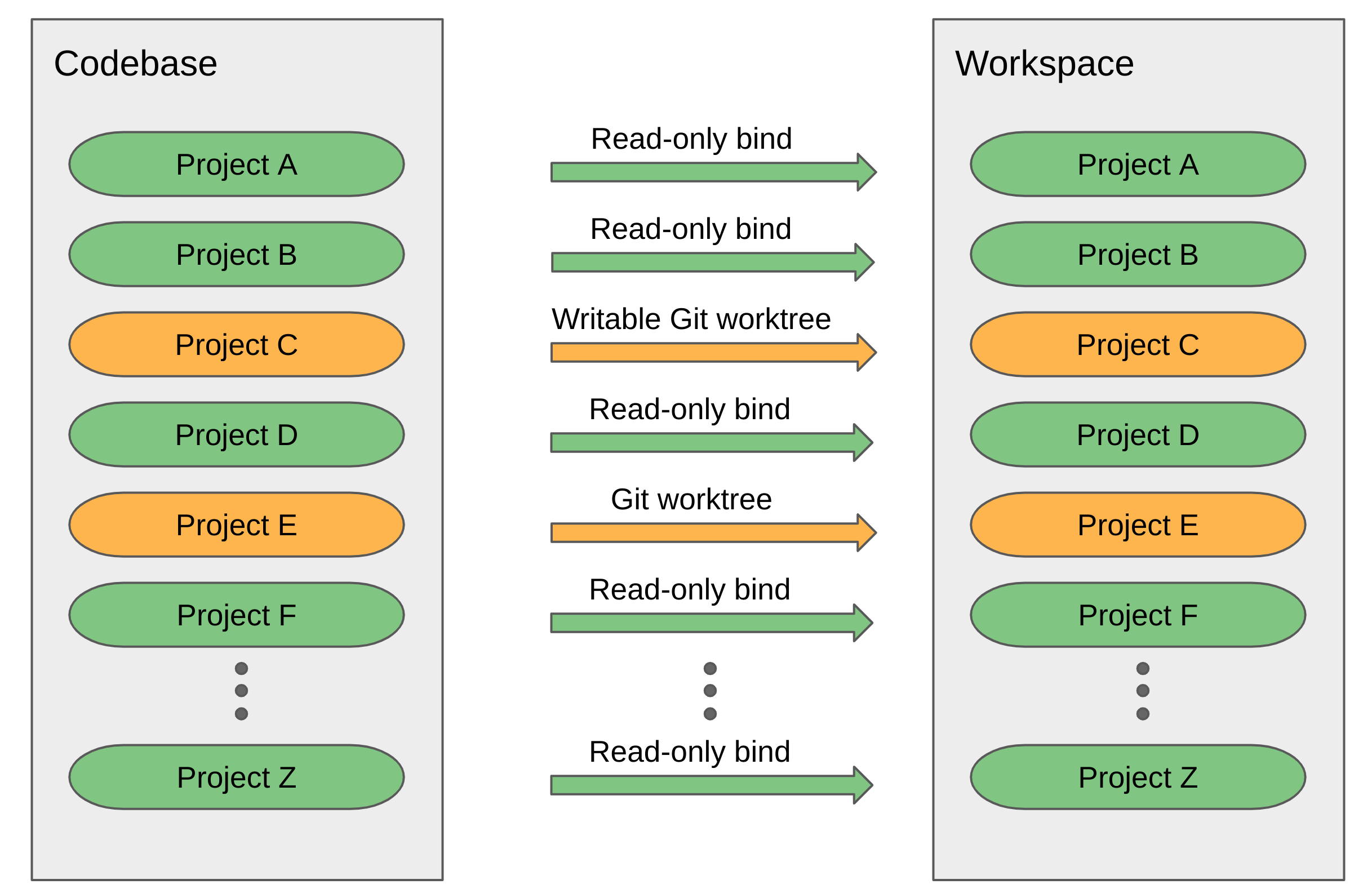
How does hacksaw work?
Hacksaw uses read-only bind mounts to create project references from a workspace to a codebase. When you mark a project for editing then its read-only bind mount gets replaced by a writable Git worktree.
What are the known issues?
- Some repo commands don't work yet. Namely:
repo startandrepo upload. So at the moment you can only upload to Gerrit using git push. - Failing to create a workspace is not rolled back.
- Editing nested projects is not supported yet. So if you have a git project that contains other git projects you will get some unexpected behaviour.
- Git submodules are not supported yet, but the tool is designed with future git submodule support in mind.
- Syncing a codebase does update the existing projects in all attached workspaces but it does not remove or add new projects. Perhaps there should be a new "workspace sync" command for that?
Where can I get more help?
You can ask hacksaw-users@googlegroups.com by joining the group.